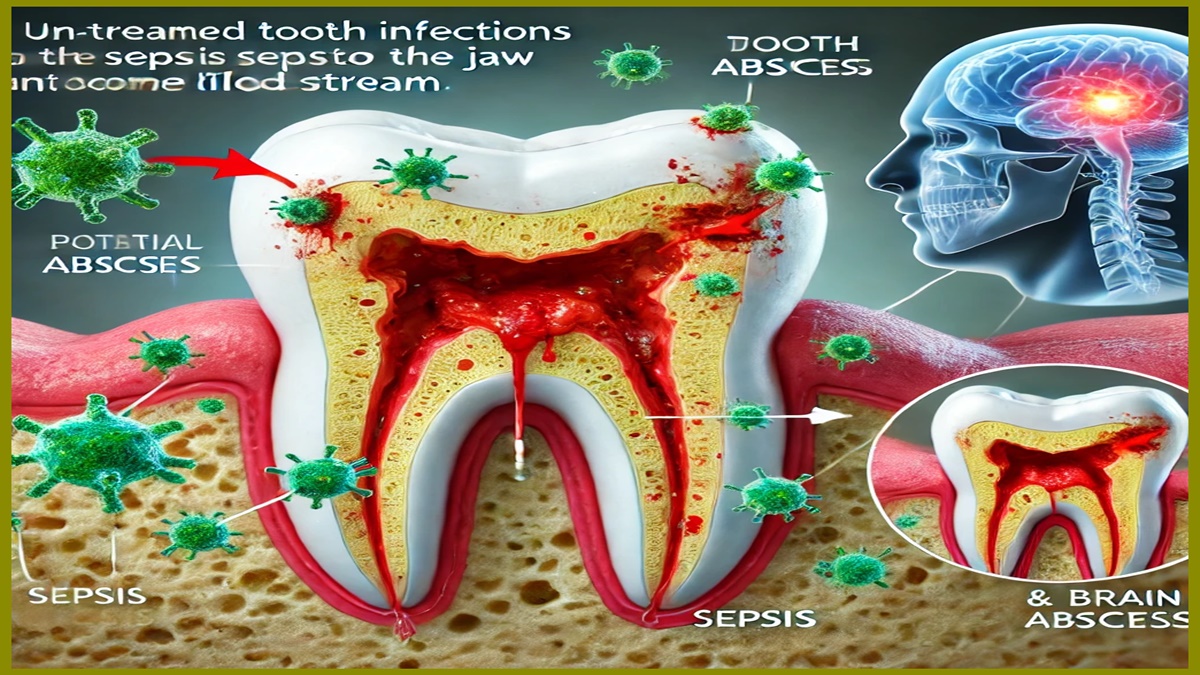
Tooth infections may seem like a minor issue, but when left untreated, they can become life-threatening. From sepsis to brain abscesses, a neglected tooth infection has the potential to cause serious harm. In this article, we’ll explore the timeline, symptoms, risks, and preventive measures related to severe tooth infections. Taking early action is key to safeguarding your health and avoiding fatal complications.
Tooth Infection Progression
Tooth infections, also known as dental abscesses, occur when bacteria invade the tooth’s inner pulp. Here’s how they develop and progress:
- Bacteria enter through a cavity, crack, or gum injury.
- The infection spreads, leading to inflammation and pus.
- Without treatment, the infection intensifies, causing pain and abscess formation.
- It can spread beyond the tooth to the jawbone, mouth, and bloodstream.
Key Takeaway: Prompt treatment prevents complications. Ignoring a tooth infection may lead to severe outcomes.

How a Tooth Infection Can Spread to the Body
Although most infections remain localized, they can spread if left untreated:
- Abscesses form at the tooth root, causing intense pain.
- Infections may reach the bloodstream, traveling to the heart and brain.
- Symptoms of a severe infection include fever, facial swelling, difficulty breathing, and swallowing.
Important Symptoms:
- Intense throbbing pain in the jaw, neck, or ear
- Swollen, red, and pus-filled gums
- High fever and swollen lymph nodes
- Difficulty chewing or opening your mouth
Risks of a Tooth Infection
A tooth infection can lead to the following complications:
- Sepsis: The infection spreads to the blood, leading to a life-threatening immune response.
- Brain Abscess: In rare cases, bacteria reach the brain, causing inflammation and pus accumulation.
- Ludwig’s Angina: Severe infection spreads to the neck, blocking airways and causing breathing difficulties.
Sepsis Symptoms:
- Rapid heartbeat, shallow breathing
- Fever or low body temperature
- Confusion and delirium
- Extreme discomfort
How Long Before a Tooth Infection Becomes Life-Threatening?
There is no fixed timeline for when a tooth infection can become deadly. Factors like age, immune system strength, and overall health determine how quickly the infection spreads. In extreme cases, untreated tooth infections can escalate to life-threatening conditions within weeks or months.
Key Factors:
- Health Condition: Compromised immune systems, chronic illnesses (like diabetes), or old age increase the risk.
- Infection Severity: Early treatment halts infection progression, while delayed intervention may require more aggressive treatments.
Treatment and Prevention of Tooth Infections
To prevent complications, immediate dental care is necessary. Treatments include:
- Antibiotics to eliminate the infection
- Drainage of the abscess
- Root canal therapy for severe infections
- Tooth extraction when the damage is too severe
Preventive care is crucial to avoid tooth infections altogether. Proper oral hygiene practices like regular brushing, flossing, and reducing sugar intake can significantly lower your risk of developing infections.

FAQs About Tooth Infections
- How long does it take for a tooth infection to spread to the brain?
- It can take weeks or months for an untreated tooth infection to spread to the brain.
- What are the first signs of a tooth infection?
- Throbbing pain, swollen gums, and sensitivity to hot and cold are the initial signs.
- Can a tooth infection lead to sepsis?
- Yes, in severe cases, untreated tooth infections can cause sepsis.
- How do you know if a tooth infection has spread to the bloodstream?
- Symptoms like fever, rapid heartbeat, confusion, and swelling in the neck are signs of a spreading infection.
- Can Listerine kill a tooth infection?
- No, mouthwash helps maintain oral hygiene but cannot cure an infection.
- Can antibiotics alone treat a tooth infection?
- Antibiotics can help reduce infection, but additional treatments like drainage or a root canal may be necessary.
- How long before a tooth infection becomes life-threatening?
- It varies by individual, but severe infections can become life-threatening within weeks if untreated.
- Is tooth infection fatal?
- While rare, untreated tooth infections can be fatal if they spread to the brain or bloodstream.
- What are the risk factors for severe tooth infections?
- Age, chronic illness, immune suppression, and poor oral hygiene are significant risk factors.
- Can a tooth infection cause breathing difficulties?
- Yes, in severe cases, swelling can block airways and cause breathing problems.
- Can a tooth infection cause permanent damage?
- Yes, untreated infections can lead to tooth loss, bone loss, and even brain damage.
- How can I prevent tooth infections?
- Maintain good oral hygiene, regular dental checkups, and reduce sugar intake.
- What happens if a tooth infection reaches the heart?
- It can cause endocarditis, a serious infection of the heart’s lining.
- Can a tooth infection cause a brain abscess?
- Yes, bacteria from the infection can travel to the brain, leading to an abscess.
- How quickly does a tooth infection progress?
- The speed of progression varies based on individual health factors and how soon treatment is sought.
- Can a tooth infection be treated with home remedies?
- Home remedies can alleviate symptoms but won’t treat the infection itself; dental care is essential.
- Why does a tooth infection cause bad breath?
- The bacteria in the infection release foul-smelling compounds, causing bad breath.
- Can a tooth infection cause facial swelling?
- Yes, facial swelling is a common symptom of a severe infection.
- Is tooth infection common among older adults?
- Yes, older adults are at a higher risk of severe infections due to weakened immune systems.
- When should I see a dentist for a tooth infection?
- Seek dental care as soon as you notice any signs of infection, such as swelling, pain, or pus.
Conclusion
Tooth infections are serious and can escalate quickly if not treated. Early intervention is crucial to prevent complications like sepsis and brain abscesses. Prioritize dental care to maintain both your oral and overall health.